River Tweed
| River Tweed | |
|---|---|
 The River Tweed at Abbotsford | |
 River Tweed watershed (Interactive map) | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Part | Scotland, England |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Tweed's Well |
| • location | Tweedsmuir, Scottish Borders, Scotland |
| • coordinates | 55°26′42″N 3°29′46″W / 55.445°N 3.496°W |
| Mouth | North Sea |
• location | Berwick-upon-Tweed, Northumberland, England |
• coordinates | 55°45′55″N 1°59′27″W / 55.7652°N 1.9909°W |
| Length | 156 km (97 mi) |
The River Tweed, or Tweed Water, Scots: Watter o Tweid, Welsh: Tuedd), is a river 97 miles (156 km)[1] long that flows east across the Border region in Scotland and northern England. Tweed cloth derives its name from its association with the River Tweed.[2] The Tweed is one of the great salmon rivers of Britain and the only river in England where an Environment Agency rod licence is not required for angling. The river generates a large income for the local borders region, attracting anglers from all around the world.[3]
Etymology
[edit]Tweed may represent an Old Brittonic name meaning "border".[4] A doubtful proposal is that the name is derived from a non-Celtic form of the Indo-European root *teuha- meaning "swell, grow powerful".[5]
Course
[edit]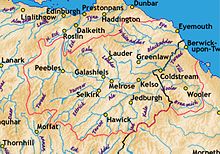
The River Tweed flows primarily through the scenic Borders region of Scotland. Eastwards from the settlements on opposing banks of Birgham and Carham it forms the historic boundary between Scotland and England.
It rises in the Lowther Hills at Tweed's Well near to where the Clyde, draining northwest (10 kilometres (6.2 mi) from the Tweed's Well), and the Annan draining south (1.9 kilometres (1.2 mi) from the Tweed's Well) also rise. "Annan, Tweed and Clyde rise oot the ae hillside" is a saying from the Border region.[6] East of Kelso, it becomes a section of the eastern part of the border. Entering England, its lower reaches are in Northumberland, where it enters the North Sea at Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Catchment
[edit]The river east of St Boswells runs through a drumlin field. It is the relic of a paleo-ice stream that flowed through the area during the last glaciation. Major towns through which the Tweed flows include Innerleithen, Peebles, Galashiels, Melrose, Kelso, Coldstream and Berwick-upon-Tweed, where it flows into the North Sea. Tweed tributaries include:
- Whiteadder Water
- River Till
- Eden Water
- Teviot Water
- Leader Water
- Ettrick Water
- Gala Water
- Leithen Water
- Quair Water
- Eddleston Water
- Manor Water
- Lyne Water
- Holms Water
The upper parts of the catchment of the Tweed in Scotland form the area known as Tweeddale, part of which is protected as the Upper Tweeddale National Scenic Area, one of 40 such areas in Scotland which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development.[7]
Management
[edit]| Tweed Fisheries Act 1771 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act for regulating and improving the Fisheries in the River Tweed, and the Rivers and Streams running into the same; and also within the Mouth or Entrance of the said River. |
| Citation | 11 Geo. 3. c. 27 |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 12 April 1771 |
| Other legislation | |
| Repealed by | River Tweed Fisheries Act 1830 |
Status: Repealed | |
| Tweed Fisheries Act 1775 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act for amending and rendering more effectual an Act, passed in the Eleventh Year of His present Majesty's Reign, intituled, "An Act for regulating and improving the Fisheries in the River Tweed, and the Rivers and Streams running into the same, and also within the Mouth or Entrance of the said River." |
| Citation | 15 Geo. 3. c. 46 |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 22 May 1775 |
Status: Repealed | |
| Tweed Fisheries Act 1797 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An act for altering, amending, and rendering more effectual two acts, made in the eleventh and fifteenth years of the reign of his present Majesty, for the regulation and improvement of the fisheries in the river Tweed, and the rivers and streams running into the same, and also within the mouth or entrance of the said river. |
| Citation | 37 Geo. 3. c. 48 |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 3 May 1797 |
| Other legislation | |
| Repealed by | River Tweed Fisheries Act 1830 |
Status: Repealed | |
| River Tweed Fisheries Act 1807 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Citation | 47 Geo. 3 Sess. 1. c. xxix |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 25 April 1807 |
| Other legislation | |
| Repealed by | River Tweed Fisheries Act 1830 |
Status: Repealed | |
| Text of statute as originally enacted | |
| River Tweed Fisheries Act 1830 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Citation | 11 Geo. 4 & 1 Will. 4. c. liv |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 29 May 1830 |
| Other legislation | |
| Repealed by | Tweed Fisheries Act 1857 |
Status: Repealed | |
| Text of statute as originally enacted | |
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act to alter, amend, and enlarge the Powers of an Act paged in the Eleventh Year of the Reign of His late Majesty, intituled "An Act for the more effectual Preservation and Increase of the Breed of Salmon, and for better regulating the Fisheries in the River Tweed, and the Rivers and Streams running into the same, and abo within the Mouth or Entrance of the said River." |
|---|---|
| Citation | 6 & 7 Will. 4. c. lxv |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 21 June 1836 |
| Other legislation | |
| Amends | River Tweed Fisheries Act 1830 |
| Repealed by | Tweed Fisheries Act 1857 |
Status: Repealed | |
| Text of statute as originally enacted | |
| Tweed Fisheries Act 1857 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Citation | 20 & 21 Vict. c. cxlviii |
| Other legislation | |
| Repealed by |
|
Status: Repealed | |
| Tweed Fisheries Amendment Act 1859 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act to amend "The Tweed Fisheries Act 1857,"[b] and to alter the Annual Close Times in the River Tweed. |
| Citation | 22 & 23 Vict. c. lxx |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 1 August 1859 |
| Other legislation | |
| Repealed by |
|
Status: Repealed | |
| Tweed Fisheries Act 1969 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act to amend the Tweed Fisheries Act 1857] and the Tweed Fisheries Amendment Act 1859; to apply certain provisions of those Acts to freshwater fish; and for other purposes. |
| Citation | 1969 c. xxiv |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 25 June 1969 |
| Other legislation | |
| Repealed by |
|
Status: Repealed | |
| Scotland Act 1998 (River Tweed) Order 2006 | |
|---|---|
| Statutory Instrument | |
 | |
| Citation | SI 2006/2913 |
| Dates | |
| Made | 14 November 2006 |
| Commencement | 15 November 2006 |
| Other legislation | |
| Repeals/revokes |
|
| Made under | Scotland Act 1998 |
Status: Current legislation | |
| Text of statute as originally enacted | |
Despite that the catchment straddles the border between Scotland and England, management of it – in terms of water quality, bio-security, and ultimately protection of the salmon of the River Tweed – is overseen by a single body, the River Tweed Commission.[8]
River Tweed Trail
[edit]As of 2024[update], work is in progress on the development of a 113-mile (182 km) walking and cycling route following the length of the river from Moffat to Berwick-on-Tweed. The work includes new sections of path, upgrades to existing paths, bridge replacement and repairs, pedestrian road crossings, lighting and signage. The path is expected to be completed during 2028.[9]
Gallery
[edit]-
The River Tweed at Abbotsford, near Melrose
-
The River Tweed from Mertoun House, near St Boswells
-
The Anglo-Scottish border, with the Tweed on the east. Its estuary and the town of Berwick-upon-Tweed were a late annexation by England.
See also
[edit]- Anglo–Scottish border
- Both sides the Tweed
- List of places in the Scottish Borders
- List of rivers of the United Kingdom
- Rivers and Fisheries Trusts of Scotland
Notes
[edit]- ^ Clayton, Phil (2012). Headwaters: Walking to British River Sources (First ed.). London: Frances Lincoln Limited. p. 193. ISBN 9780711233638.
- ^ "Article on Tweed Cloth". Archived from the original on 16 December 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ^ "Wild fishing tax 'raid' concern". BBC News. 10 August 2015.
- ^ "University of Wales Dictionary". University of Wales Dictionary. University of Wales. Archived from the original on 31 May 2019. Retrieved 4 June 2019.
- ^ James, Alan. "The Brittonic Language in the Old North - A Guide to the Place-Name Evidence" (PDF). Scottish Place Name Society.
- ^ The Tweed: Take a trip on a river flowing with history Archived 2019-07-31 at the Wayback Machine, The Independent, 21 April 2007
- ^ "National Scenic Areas". Scottish Natural Heritage. Archived from the original on 18 January 2018. Retrieved 17 January 2018.
- ^ "History of the RTC". www.rivertweed.org.uk/. Retrieved 22 February 2022.
- ^ McDougall, Mark (28 October 2024). "'Ambitious' Destination Tweed project granted £10 million of new funding". The Herald. Retrieved 29 October 2024.
External links
[edit]- British Waterways: River Tweed
- The River Tweed Commission website Archived 6 January 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- The Tweed Foundation
- Tweed Forum website
- River Tweed: Special Area of Conservation (SAC)
- SEPA (Scottish Environment Protection Agency): River Level Data Archived 24 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- River Tweed map
- Gazetteer for Scotland: River Tweed
- Paper describing palaeo-icestream and landforms in the Tweed Valley
- Map and aerial photo sources for Tweed's Well and Tweedmouth
- Open Canoe Hire Specialists
- River Tweed
- Rivers of Northumberland
- Rivers of the Scottish Borders
- Anglo-Scottish border
- Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Annandale and Eskdale
- Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Berwickshire and Roxburgh
- Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Mid and East Lothian
- Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Tweeddale and Ettrick and Lauderdale
- Tweed catchment




